Have you ever noticed bruises appearing out of nowhere? Those black-and-blue marks can be unsightly, sometimes painful, and occasionally a sign of an underlying health issue. Today, we’ll explore why bruising happens, how to prevent it, and when it might indicate something serious. Here’s a hint—certain vitamin deficiencies could be a factor.
What is Bruising?
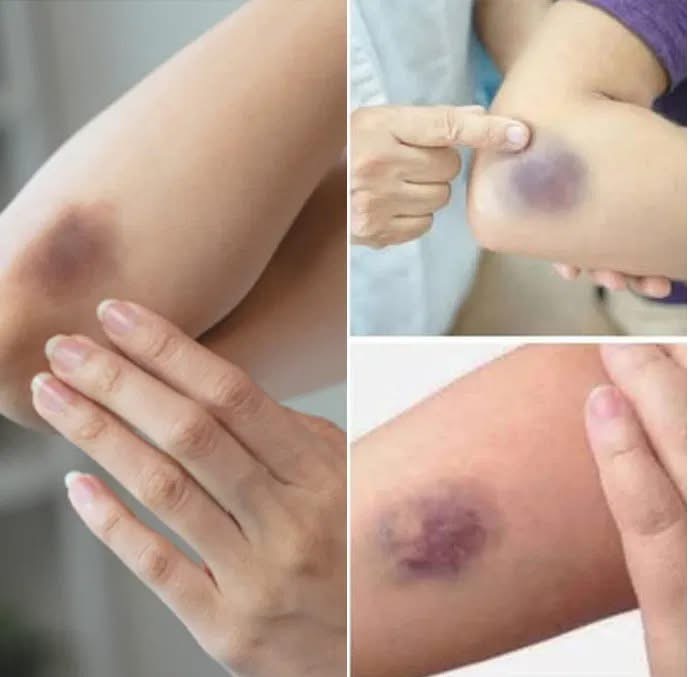
The medical term for bruising is ecchymosis. It occurs when small blood vessels beneath the skin break, causing blood to pool under the surface. Unlike cuts, where blood escapes, bruises stay under the skin and change color as they heal—from red or blue to purple, then green or yellow, before fading.
Most bruises result from minor injuries, like bumping into something. However, some people bruise more easily due to health conditions or deficiencies.
When Should You Be Concerned?
While occasional bruises are normal, see a doctor if you notice:
Frequent bruising without a clear cause
Bruises that take longer than two weeks to heal
Bruises in unusual areas like the stomach, ears, or genitals
Vitamin Deficiencies That Can Cause Bruising
Vitamin C Deficiency – Weakens blood vessels, making bruising more common. Eat more citrus fruits, tomatoes, and broccoli. Smokers are especially at risk.
Vitamin K Deficiency – Affects blood clotting, leading to frequent bruising.
Vitamin D & B Deficiencies – Can also contribute to bruising. If you suspect a deficiency, consider testing your levels.
Supplements That May Increase Bruising
Certain supplements thin the blood, making bruising more likely:
Ginkgo, ginseng, ginger, and garlic
Omega-3 fatty acids
Vitamin E
Saw palmetto
Leave a Reply